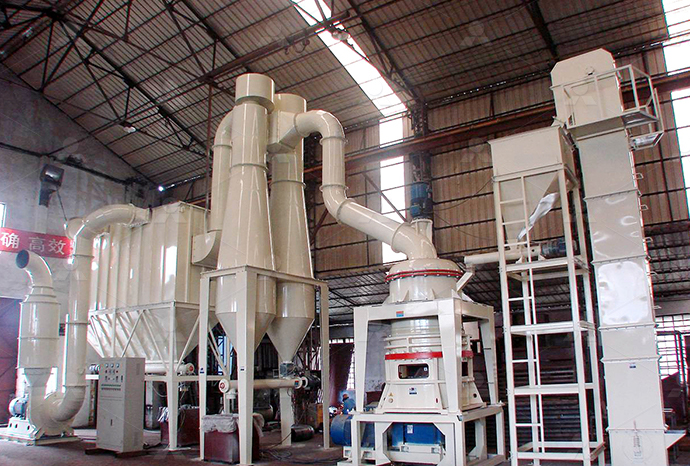
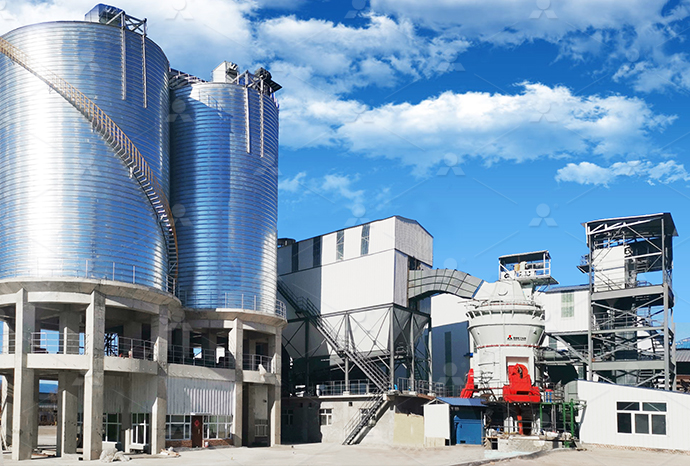
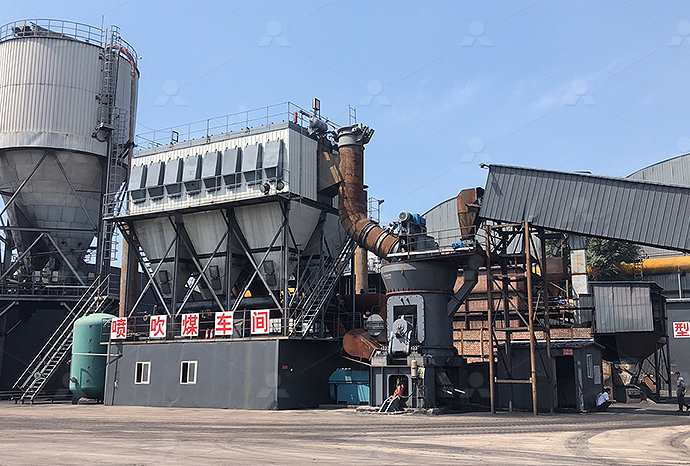
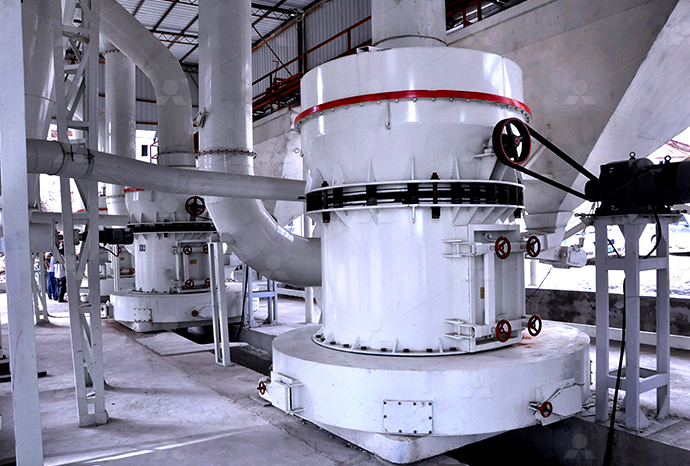
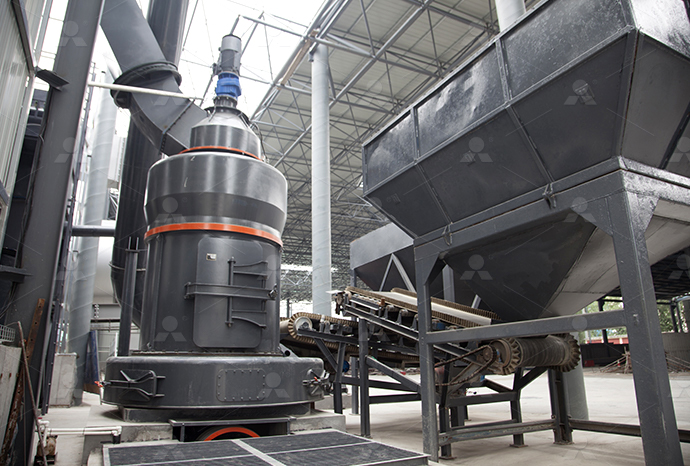
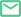
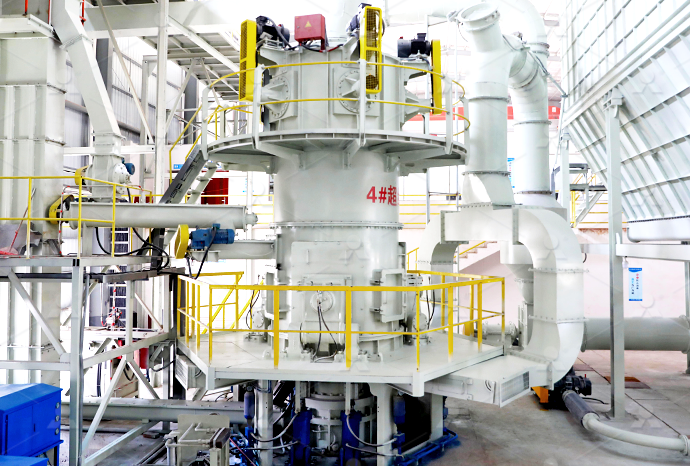
Find equipment for cutting large stones into flakes

What Machines Do Stone Crushing Plants Need?
2024年10月14日 What machines are required for a stone crusher plant, and what is the function of each? Here, you'll discover 11 stone crushing equipment needed for stone crushing, from primary crushers to fine crushers and Hardhammer percussion is essential for breaking up larger stones into flake blanks and cores, and it was used in early stages of reduction in even the most complex technologies 'Direct' hardhammer percussion refers to a technique Flake Scars and Flaking Techniques Museum of 2024年6月6日 Primary crushers are used to break down large stones into smaller, manageable pieces Common types include jaw crushers and gyratory crushers Jaw crushers use compressive force to crush the stone between two Essential Guide: Types of Machines Used in 2024年11月26日 Explore the equipment used to transform large rocks into fine crushed stone Learn about the best machinery for efficient crushing operationsTransforming Rocks into Fine Crushed Stone:

Types of Crushers: Choosing the Right One for
2024年7月17日 A crusher, also known as a stone crusher, is a machine that uses mechanical action to break large rocks, ores, or other raw materials into gravel or rock powder Crushers are widely used in ore crushing, aggregate 2024年8月7日 Elements of tool standardization appear relatively early in the Lower Paleolithic, including the differentiation between a back (or prehensile portion) and an active cutting edge Large cutting tools (bifaces and flake Back(s) to basics: The concept of backing in Simple cores and flakes persisted right up until the present day, with more elaborate stoneflaking technologies appended onto this simple foundation Reducing a core can involve strategic planning, by striking off flakes in a Cores and Flakes Museum of Stone Tools4 天之前 Our Hydraulic stone splitting machine is suitable for splitting all types of natural and artificial stones, cube stone/curb stone/wall Hydraulic Stone Splitting Machine StoneContact
.jpg)
How to Create Stone Tools; Flintknapping Techniques
Percussion Techniques A set of methods using a billet or hammerstone to strike and remove unwanted flakes from a piece of knapping stone Most commonly used for thinning medium to In making a stone tool, the stoneworker, or ‘flintknapper’, strikes flakes from a core A core is, technically, any stone from which flakes have been removed—this can include cobbles and chunks of stone, or flakes that were struck previously Workshop 1 Cores and Flakes Museum of 2024年11月26日 Other types of bladelike flake tools were created from a stone with a flat surface where people would use antler, bone, or other hard materials to punch or directly knock flakes or blades from the stone/core Flakes are also 7 Types of Stone Tools Used by Our Ancestors2024年5月25日 The Stone Age began around 26 million years ago, when researchers discovered the earliest evidence of humans using stone tools The production of these tools involved a complex sequence of steps, including the removal of large flakes from a core, the shaping of the flakes into a symmetrical form, and the final retouch of the edgesThe Stone Age Toolkit: A Historian‘s Perspective on

How To Start Gem Cutting (Beginner's Guide)
2024年1月27日 Grind the stone into a dome shape using grinding wheels; Sand and polish for a smooth, glossy finish; Remember, the height of the dome and the symmetry of the cabochon are crucial for aesthetic appeal Practice Your This beginner’s guide to identification of knapped flints and stone tools has been written by Barry Bishop and is one of a series of introductory guides published by the community archaeology network, Jigsaw The aim of this guide is to help in recognising flint tools and in distinguishing deliberately modified from naturally occurring rocksIdentification of knapped flints and stone tools2024年8月7日 On the other hand, backed knives are common among Acheulean large cutting tools Usually made on large flakes and with pointed or crescentlike morphologies, these tools are characterized by asymmetrical crosssections defining a backed edge, which could originate either from cortical surfaces, fracture planes in raw materials, striking Back(s) to basics: The concept of backing in stone tool A core is, technically, any stone from which flakes have been removed—this can include cobbles and chunks of stone, or flakes that were struck previously and then further reduced Most archaeologists, however, refer to flakes that have been further reduced as retouched flakes , or by their typological classification (eg, ‘Tula Adze’)Workshop 1 Cores and Flakes Museum of Stone Tools
.jpg)
SLICERS, FLAKERS FoodTechProcess
2024年4月29日 Slicers and flakers are used for consistently cutting and dicing products into uniform sizes Slicers and flakers are essential tools in the food processing industry, offering precise cutting, slicing, and flaking of various ingredients These machines play a vital role in transforming raw materials into uniform slices, flakes, or pieces, enhancing the efficiency, Flakes were sometimes retouched to create tools with a specific shape For instance, a Neolithic tool called a ‘fan scraper’ was retouched by percussion or pressure flaking applied to one face These were traded widely in northeast Africa and Western Asia Similarly, Aboriginal people in the recent made ‘tula adzes’—a type of retouched flake—and exchanged them for a narcotic plant Retouched Flakes Museum of Stone ToolsArcheologists find stone tools on all the planet's habitable landmasses, even in its cold and ecologically For over a century, archeologists and amateur prehistorians broke rocks to gain insight into stonetool technologies This field is broadly referred to as experimental archaeology and involves the act of replicating processes of stone (PDF) Stone Tools: Their Relevance for Historians and the It is characterised by the production of long, thin stone flakes that were shaped into long blade knives, spearheads and other tools Mode 5 was a more advanced technology than Mode 4 and specialised in the production of very small blades (microliths) that were often used in composite tools having several plex technology The Australian Museum
.jpg)
Flintknapping Tools Museum of Stone Tools
Hammerstones are the most common flintknapping tool in the archaeological record These tools were often highly prized because it can be difficult to find a stone of the appropriate shape, weight, and material to suit various flaking 2024年2月2日 Diving into the world of stone cutting can be both exhilarating and daunting Whether you're looking to craft a unique piece of jewelry, create stunning As you delve deeper into stone cutting, specialized equipment like Beginner's Guide to Stone Cutting: Tools Tips The most common technique of leasteffort flaking is using a hammerstone to strike flakes from a core Removing one flake creates suitable surfaces for removing the next flake When the core is flipped and rotated between these Cores and Flakes Museum of Stone Tools2018年4月1日 The diversity of chipped stone technologies found in the past 33 million years are based, in large part, on iterations of the same operation, flake removal, chained together in different ways [6 (PDF) Two million years of flaking stone and the evolutionary
.jpg)
How Did People Make Flaked Stone Tools? Archaeology
The flake is the most basic element in flintknapping, and a flake is struck from a rock called a core A flake generally has very sharp edges, making it useful for cutting, scraping, and carving Some flakes are worked into projectile points for an atlatl or bowThe stoneworker applied oblique force because the expanding flake would tear away part of the tool’s platform edge This created an arris to guide the next flake, which also would tear away the adjacent part of the platform edge When applied in series, this ‘tearing’ effect could create an extremely sharp edge—indeed, this is the sharpest edge possible using a retouching techniquePressure Flaking Museum of Stone Tools2017年9月10日 This mediation allowed you to have precise targeting of force, and still have all the momentum of a falling hammer stone going into the movement This is called indirect percussion flaking Still greater precision was achieved through pressure flaking (pressing against a stone until a flake pops off) Typically pressure flaking was used to Jordan: Basic Stone Tools University of California, San Diego2023年9月20日 These studies only investigate a few Early Stone Age (ESA) and Lower Palaeolithic (LP) technologies, and although flakes and large cutting tool (LCT) bifaces characterise two to three million Hafted technologies likely reduced stone toolrelated

(PDF) Wild monkeys flake stone tools ResearchGate
2016年10月19日 Examples of flaked stones from capuchin SoS percussion a, Detail of a large, unidirectionally flaked active hammerstone, with clear impact marks located towards the centre of the striking 2024年4月6日 The presence or absence of handaxes endures as the major criterion of Lower Palaeolithic classification, with contemporaneous coreandflake industries modelled as simpler counterparts to Acheulean technology This is based on the supposed absence of formal tools, particularly of large cutting tools (LCTs) which are understood to be important within Not Just Scraping By: Experimental Evidence for Large Cutting 2018年3月10日 A hammerstone (or hammer stone) is the archaeological term used for one of the oldest and simplest stone tools humans ever made: a rock used as a prehistoric hammer, to create percussion fractures on another rock Hammerstone: The Simplest and Oldest Stone A microlith is a small stone flake, less than ca 30 mm long, that was mounted onto a shaft or handle The sharp, exposed edge of the microlith was the cutting element Microliths were mounted individually or were arranged in a line to Microliths Museum of Stone Tools
.jpg)
CHAPTER 3 CHIPPED STONE—ILAIYARNGASQAQ
2024年2月8日 flakes), using a small flaking tool (eg, a pressure flaker) By documenting the presence of cortex, the size and weight of flakes, researchers can sometime determine the stage of chipped stone manufacturing represented in an assemblage For example, large heavy flakes with cortex suggest earlystage manufacturing, the reduction of a cobble2009年1月30日 lines the work, introduces the Acheulean, and defines large cutting tools (LCTs) and largeflake based (LFB or on flakes larger than 10 cm) Acheulean industries Typology is an important focus of this chapter although Sharon himself (rightly) is not clear about some distinctions (eg, specimens ‘h’ and ‘f’ on page 19)Acheulian Large Flake Industries: Technology, Oldowan industry (Earlier Stone Age) Tool Types: The Oldowan industry was the earliest of all stone tool technologies, emerging just after 26million years ago, during the Earlier Stone Age Simple flakes were the most important tool type Cores (the rocks off which the flakes are chipped) included those shaped as choppers (flaked along an edge), discoids (flaked to a disk Stone tools – Maropeng and Sterkfontein Caves2024年9月25日 These tools were made by carefully striking flakes off a stone core, resulting in sharp edges that could be used for cutting, scraping, and piercing Technology And Techniques Used In Crafting Stone Tools: Knapping: Early humans used a technique called knapping to shape stones into tools This involved carefully striking a stone core with Ancient Indian Artifacts Stone Tools: Hand Axe, Cleavers!

How to Cut Large Size Stone Blocks MosCut Stone Machine
The craft of cutting large stone blocks has been refined over centuries, evolving from the laborious hand chiseling of ancient stonemasons to the sophisticated machinery used today The ability to precisely cut stone is crucial in various industries, from construction and landscaping to sculpture and masonry This article explores the various kinds of equipment designed for stone block Oversize 6+ inch Spalls Large Flat Rate Box Free Shipping Limited time offer for rare oversize material while supplies last Large USPS Flat Rate box packed with 20 pounds of our #1 graded and cleaned 6+ inch 'extralarge' spalls Box price includes shipping within View full Flintknapping Stone Spalls, Flakes, Raw RockBeginner’s Guide to Lapidary as a Hobby: Mastering the Art of Stone Cutting and Polishing Lapidary, the art of cutting, shaping, and polishing stones and gemstones, offers a unique combination of craftsmanship and science It can turn rough natural treasures into stunning pieces of jewelry or ornamental objectsBeginner's Guide to Lapidary: The Art of Stone Cutting2024年11月26日 Other types of bladelike flake tools were created from a stone with a flat surface where people would use antler, bone, or other hard materials to punch or directly knock flakes or blades from the stone/core Flakes are also 7 Types of Stone Tools Used by Our Ancestors

The Stone Age Toolkit: A Historian‘s Perspective on
2024年5月25日 The Stone Age began around 26 million years ago, when researchers discovered the earliest evidence of humans using stone tools The production of these tools involved a complex sequence of steps, including the removal of large flakes from a core, the shaping of the flakes into a symmetrical form, and the final retouch of the edges2024年1月27日 Grind the stone into a dome shape using grinding wheels; Sand and polish for a smooth, glossy finish; Remember, the height of the dome and the symmetry of the cabochon are crucial for aesthetic appeal Practice Your How To Start Gem Cutting (Beginner's Guide)This beginner’s guide to identification of knapped flints and stone tools has been written by Barry Bishop and is one of a series of introductory guides published by the community archaeology network, Jigsaw The aim of this guide is to help in recognising flint tools and in distinguishing deliberately modified from naturally occurring rocksIdentification of knapped flints and stone tools2024年8月7日 On the other hand, backed knives are common among Acheulean large cutting tools Usually made on large flakes and with pointed or crescentlike morphologies, these tools are characterized by asymmetrical crosssections defining a backed edge, which could originate either from cortical surfaces, fracture planes in raw materials, striking Back(s) to basics: The concept of backing in stone tool

Workshop 1 Cores and Flakes Museum of Stone Tools
A core is, technically, any stone from which flakes have been removed—this can include cobbles and chunks of stone, or flakes that were struck previously and then further reduced Most archaeologists, however, refer to flakes that have been further reduced as retouched flakes , or by their typological classification (eg, ‘Tula Adze’)2024年4月29日 Slicers and flakers are used for consistently cutting and dicing products into uniform sizes Slicers and flakers are essential tools in the food processing industry, offering precise cutting, slicing, and flaking of various ingredients These machines play a vital role in transforming raw materials into uniform slices, flakes, or pieces, enhancing the efficiency, SLICERS, FLAKERS FoodTechProcessFlakes were sometimes retouched to create tools with a specific shape For instance, a Neolithic tool called a ‘fan scraper’ was retouched by percussion or pressure flaking applied to one face These were traded widely in northeast Africa and Western Asia Similarly, Aboriginal people in the recent made ‘tula adzes’—a type of retouched flake—and exchanged them for a narcotic plant Retouched Flakes Museum of Stone ToolsArcheologists find stone tools on all the planet's habitable landmasses, even in its cold and ecologically For over a century, archeologists and amateur prehistorians broke rocks to gain insight into stonetool technologies This field is broadly referred to as experimental archaeology and involves the act of replicating processes of stone (PDF) Stone Tools: Their Relevance for Historians and the

Complex technology The Australian Museum
It is characterised by the production of long, thin stone flakes that were shaped into long blade knives, spearheads and other tools Mode 5 was a more advanced technology than Mode 4 and specialised in the production of very small blades (microliths) that were often used in composite tools having several parts